What is compliance management?
Business regulation is a growing concern for companies of every size and industry. Compliance management programs check a company’s adherence to internal and external regulations. This includes internal controls, applicable laws, tax and finance regulations, and relevant industry standards.
The goal of compliance management is to ensure the organization operates responsibly and legally. It applies not just to financial planning and analysis (FP&A), but to every aspect of a company's operations.
For FP&A, compliance management ensures that financial activities in the company align with all applicable laws and regulations. These financial activities include:
- Accounting
- Taxation
- Budgeting
- Auditing
- Reporting
Companies must have systems in place to monitor financial activities continuously. Internal policies and processes guide individual decisions and team activities, help identify errors or fraud, and outline how (and to what agencies) the company must demonstrate compliance.
Ultimately, compliance management helps companies protect their reputation and avoid costly fines or lawsuits. Staying up-to-date with the relevant laws and regulations ensures organizations can minimize risk while achieving their desired results.

What are the costs of non-compliance?
Non-compliance—even unintentional instances or infractions—leads to various legal, financial, and reputational consequences. Depending on the type of regulation or issue, companies that have outstanding or ongoing issues with non-compliance may:
- Pay fines or penalties for individual infractions
- Face litigation or censure from regulatory bodies
- Lose good standing in regulatory reporting databases
- Have their business activities restricted
- Attract customer complaints or reputational damage
In the worst cases, non-compliance can result in criminal charges, jail time for senior executives, and even dissolution of the organization.
The most basic cost of non-compliance, though? Lower productivity. When teams must focus on researching and remedying non-compliance, they cannot focus on their primary mission of creating value for shareholders and other stakeholders.
What types of compliance do FP&A teams manage?
As Finance becomes a closer strategic partner to the executive team, its areas of responsibility within the business grow. Since these teams oversee and monitor the financial life of the company, they are also the key contact for many areas of compliance management:
Financial
Financial compliance ensures that company financial reporting practices align with rules set by regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This means providing accurate, timely, and complete info about assets, liabilities, revenue, and cash flow. Companies must ensure internal records align with public disclosures while adhering to corporate governance and conduct codes. These compliance responsibilities are present for every company and even more important for publicly traded companies.
Accounting
Accounting compliance means adhering to accepted standards for preparing financial data. The main standards are Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States and the International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) worldwide.
GAAP is a set of guidelines companies must follow while preparing financial statements. IFRS are similar standards issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). GAAP and IFRS are globally recognized, enabling an easy understanding of financial documents. Each standard promotes consistent financial reporting among industries to protect against unintentional errors and fraud. During audits, businesses must verify their financial records are compliant with these regulations.
Taxation
Tax compliance ensures companies adhere to domestic and international tax laws issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the International Bureau of Fiscal Documentation (IBFD). These bodies monitor businesses through audits, review of tax returns, and other monitoring relevant to the business and its domestic and international activity.
These agencies can request records from third parties, such as banks or vendors, to verify the accuracy of information submitted by taxpayers. Businesses must keep up-to-date records of their finances to provide accurate information and documents upon request by the IRS or other entities.
Data security
As finance moves into the cloud, data security and privacy come under increased scrutiny and regulation. Data security compliance is a process that helps organizations protect their data from unauthorized access, accidental or malicious destruction, and other forms of misuse. It involves monitoring preventive security measures such as:
- Data encryption
- Network access
- Virus detection
- Penetration testing (hack testing)
- Data destruction management
Laws such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) set the standards for how organizations manage compliance with data protection regulations. These laws require certain measures when dealing with customer and employee data, such as ensuring that information is stored and managed securely. These bodies may impose penalties for violations, including financial fines and other legal recourse.
What are the components of a compliance management program?
While some of the above compliance categories apply to all companies, the details of a compliance program are often unique to the organization. The categories and levels of monitoring will vary depending on your organization’s structure, industry, size, and ownership (private versus publicly owned).
Despite these differences, every organization will build its compliance program on a common foundation. These core components will ensure your compliance activities and outcomes remain strong:
Policies and procedures
The first step in any compliance program: get it all in writing. Documenting your compliance procedures and internal policies is vital to building a culture of compliance.
Policies should be specific to the type of business activity, industry, and regulatory body in which a company operates. For example, a company providing services may have different policies than a company selling products. A compliance officer or automation system ensures that all documents stay updated when laws or regulations change. Clear, well-maintained policies and procedures prevent mistakes during compliance audits, improve team communication, and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Monitoring and risk assessments
Monitoring systems ensure internal and external stakeholders comply with the stated policies and procedures. Automated compliance monitoring systems with real-time alerts can detect compliance issues as soon as they occur, allowing companies to respond quickly to any potential problems. These reports and alerts make the auditing process less stressful and more efficient, allowing the company to address outstanding issues before they are discovered and documented during an audit.
Risk assessment is another critical component of monitoring. It provides an overview of the various risks associated with business activities and helps companies determine what measures are necessary to achieve compliance.
Risk assessments should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the regulatory environment or business operations. Companies should also develop specific protocols for responding to risks identified through risk assessment. This type of reporting provides valuable insight into opportunities for growth and optimization.
Auditing and reporting
A robust auditing and reporting process ensures that risks identified through the assessment process are correctly documented and addressed. Auditing and reporting practices should be designed to verify compliance methods are functioning as intended.
Audit and reporting programs let companies avoid potential concerns or actual non-compliance. It allows them to take corrective action before a variance becomes a problem (or worse, a fine). Auditing and reporting software provides an objective review of the company’s operations, paving the way for better experiences for internal stakeholders, customers, partners, regulators, and others.
Training
Education is key to ensuring that all employees know the company’s compliance management processes and can apply them effectively. Training on risk assessment, auditing, and reporting should be undertaken regularly so that employees have an up-to-date understanding of their responsibilities and how to adhere to them.
Companies should also consider providing continuing education on important topics like data privacy, information security, record-keeping, etc. Education is the single best tool for building a proactive compliance culture from entry-level staff right up to senior management.
What does automated compliance management entail?
Automated compliance management is a multifaceted approach that involves the use of technology (OneTrust, MetricStream, etc.) to streamline, monitor, and control compliance activities across an organization.
It entails:
- Automated workflows: Automated compliance management systems enable the creation of automated workflows to manage various compliance-related processes. From data collection to reporting and auditing, automation helps in reducing human errors and accelerates the processing time.
- Real-time monitoring: These systems continuously monitor compliance status, scanning for any deviations or potential violations. If any inconsistencies are detected, real-time alerts are sent to the concerned personnel, allowing for immediate action. For FP&A, this means immediate insights into financial discrepancies or deviations from prescribed regulatory guidelines.
- Integrated regulatory database: Automated compliance management is often integrated with up-to-date regulatory databases, ensuring alignment with the latest laws and regulations. This is vital for FP&A leaders to maintain adherence to evolving financial regulations.
- Risk assessment and management: Through intelligent algorithms, these systems can identify, assess, and manage risks associated with regulatory compliance. This allows organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate potential risks and align compliance strategies with overall risk management goals.
- Collaboration and communication tools: These systems foster cross-departmental collaboration by centralizing compliance information and providing shared access to relevant documents, deadlines, and responsibilities.
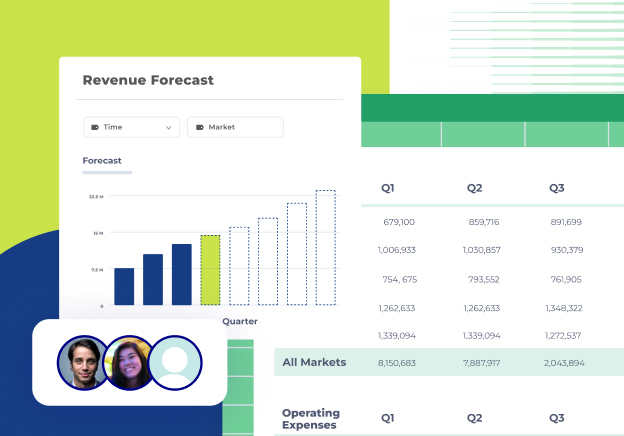
- Customizable reporting: Tailored to the unique needs of FP&A, the system offers customizable reporting options, allowing for in-depth analysis of compliance metrics and trends.
- Scalability and flexibility: Whether dealing with local regulations or international standards, this system can adapt to different regulatory environments, making it suitable for FP&A operations of various scales and geographies.
In the world of FP&A, where precision, agility, and foresight are key, an automated compliance management system is not just a tool but a strategic ally. It encapsulates the fusion of regulatory intelligence with technological innovation, paving the way for compliance management that's not only robust but also resonant with the dynamic needs of financial planning and analysis.
Is an automated compliance management system the same as FP&A software?
FP&A software and Automated Compliance Management Systems (ACMS) are distinct types of tools, but they can be closely related, especially in industries where compliance with financial regulations is critical.
FP&A software focuses on financial planning, budgeting, forecasting, and analysis. It helps businesses understand their financial performance, make informed business decisions, and align their strategies with organizational goals. FP&A software may include features to manage and analyze financial data, create financial models, and generate reports and visualizations.
ACMS, on the other hand, centers on managing and ensuring compliance with various legal, regulatory, and organizational standards. It includes features such as real-time monitoring, alerts, risk assessments, audit trails, and integration with regulatory databases, as described earlier.
Now, where the overlap occurs:
- Integration with FP&A: Many organizations must comply with financial regulations, governance standards, and reporting requirements. In such cases, an ACMS could be integrated with FP&A software to automate compliance tasks related to financial data and reporting.
- Compliance features within FP&A: Some FP&A software may include compliance management features or modules, especially those designed for industries with strict financial regulations. In this context, FP&A software might indeed serve as a type of ACMS.
- Enhanced efficiency and accuracy: By automating compliance-related tasks within the financial planning and analysis process, organizations can ensure that their financial practices are aligned with relevant regulations and standards without adding administrative burdens.
So while FP&A software and ACMS are designed for different primary purposes, they can be complementary or even integrated in environments where financial compliance is a key concern. Depending on the specific needs and regulatory landscape of a business, an FP&A system could indeed be part of or function as an ACMS.
Now that we have laid the foundation of what an automated compliance management system entails, let's dive into the specific benefits it offers in the context of FP&A.
7 benefits of automating your compliance program
Good compliance is the cornerstone of good business. Compliance isn’t just for keeping the business out of hot water. It also lends itself to better operation and higher standards across the board. Savvy enterprises use compliance to gain these key benefits in their organizations:
1. Higher accuracy
Automating your compliance process leads to greater accuracy in financial reporting by reducing human error. Automation allows accurate tracking and reporting of financial data, along with real-time updates to ensure information is always up-to-date. This means fewer issues and better audits.
2. Cost reduction and avoidance
Manual compliance practices are time-consuming. Repetitive tasks like data entry, document retrieval, and internal auditing drive up costs. Automated systems provide more accurate reporting automatically. It also reduces errors, helping companies achieve better compliance and avoid fees and penalties.
3. Visibility
Transparent data is the best way to reduce risk and ensure compliance. Automating your financial data helps organizations maintain management oversight and avoid costly data siloes. It allows teams to accurately track and report data. This ensures information is always current and accessible, enabling organizations to make informed decisions quickly. Automation also reduces errors, helping companies achieve better compliance and reducing the risk of fines or penalties.
4. Early notice
Automation can help organizations stay informed of potential financial issues as soon as they arise. These systems continually monitor for discrepancies and generate notifications when something unexpected happens. This instant notice helps companies use their data to take action.
5. Data security
When a cybersecurity issue or data breach occurs, seconds matter. Automated alerts and early detection lets companies respond to potential issues sooner. This fast action can save millions in fees and losses.
6. Streamlined reporting
Reporting obligations in finance grow by the day. Depending on the size and location of an organization, compliance or FP&A teams may be responsible for hundreds of filings and compliance dates. Automated systems aggregate data from multiple sources, creating real-time reports and dashboards quickly. This allows companies to deliver timely information to stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
7. Increased productivity
Automation eliminates tedious manual tasks and saves time. This leaves employees free to focus on higher-value activities such as research or analysis, which can help drive the business forward. Automation also reduces the training required for new staff, allowing organizations to onboard quicker and more efficiently.
Steps to prepare for a compliance audit
Need to prep for an upcoming audit? If you don’t yet have compliance automation in place, take these steps to get organized and perform a smoother, error-free audit:
1. Create a compliance audit checklist
Checklists are essential to completeness in an audit. A strong checklist will help you organize the data associated with the audit into categories relevant to the regulations being audited. For example, financial audits may look at data from income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, etc.
Identify areas with potential risk or non-compliance and compile a checklist. These checklists should include specific questions about each part of the regulation so team members can easily follow them during an audit.
It's also important to have records from prior audits for comparison purposes. Once the checklist is in place, create a schedule for conducting the audit that includes tasks such as:
- Reviewing regulatory documentation
- Interviewing relevant staff members
- Pulling past reports
- Responding to compliance findings
- Verifying financial statements for accuracy
- Reviewing internal controls
- Analyzing accounting data
- Examining contractual agreements
Following a well-defined plan and checklist will make it easier to produce accurate results and reduce the amount of time needed to complete an audit.
2. Assign roles and identify stakeholders
Financial audits often involve multiple personnel within a department or organization. Dual control – where two people review the same document or process separately and compare notes – is a popular approach.
Once the duties are assigned, it's important to involve the right stakeholders in the audit process. These may include:
- Internal auditors
- Finance team members
- Legal counsel
- Auditors from external firms
Each participant should have a clear understanding of their role and responsibilities, as well as the timeline for completion.
3. Gather relevant documentation
Once you know the data you need, create a centralized filing system for easy access. Include past reports, regulatory guidance, and other relevant documents that will help you review the compliance requirements.
4. Assess changes to laws or regs
Get familiar with what has changed since the last audit you performed. This is done by researching the latest legislature and comparing it with existing policies. Regulatory guidebooks published by relevant regulatory bodies may provide information and clarify questions.
All discrepancies should be documented in your compliance report or communicated to your audit team. For external audits, this documentation helps teams make recommendations on adhering to updated regulations.
5. Take proactive steps to remedy non-compliance
Wherever possible, document and take steps to correct non-compliance issues flagged during your audit. This may include updating policies, creating new ones, or modifying processes.
Ensure all changes are communicated to the relevant stakeholders and processes are implemented for ongoing monitoring and review.
Create any reports or filings that show that you’ve remedied outstanding audit issues, and be sure to centralize this new data in your compliance filing system for use in future reporting activities.
Bonus step: Develop a plan for improving your next audit
The best time to get started on improving your compliance program is when you’ve completed the steps necessary to conclude an audit. After all, it’s easier to stay compliant than to get compliant. A compliance management program makes every future audit easier, cleaner, and more successful.
Why is now the time? At this point, you have centralized and cleansed your data, gotten up to date on changes to regulations, completed the necessary filings, ensured your good, and taken any corrective actions necessary to bring your business processes into compliance. You’ve done most of the hard work, so you’re well-positioned to continue improving.
Conclusion: reap the benefits of compliance management
The importance of a robust compliance management program cannot be overstated. Automation in compliance not only safeguards against legal pitfalls but also streamlines operations, enhances accuracy, and fosters productivity.
By integrating best practices and employing automated systems, companies can navigate the complex landscape of compliance with confidence and efficiency. The steps and benefits outlined in this blog serve as a blueprint for organizations looking to fortify their compliance program and remain on the cutting edge of responsible and successful business management.
Want to learn how Cube can help you on this journey? Request a free demo today.


.png)



.png)