What is automated financial reporting?
Automated financial reporting uses specialized software or artificial intelligence (AI) to generate financial reports for businesses efficiently. FP&A teams rely on this software to:
- Execute account reconciliation
- Automate monthly close and data entry
- Prepare financial statements and management reports
With automated financial reporting, FP&A teams eliminate the need to sift through multiple systems or paper trails to update financial statements. Instead, the software automatically pulls data from various systems, including legacy ones, to quickly generate reports. Additionally, the system logs every activity, making audit trails easy to access and share.

Let’s take a look at the benefits of automating financial reports for FP&A teams:
Higher productivity and faster approvals
Automating financial reports means accountants can free up their time from manual data entry, report generation, and reconciliation tasks. This shift allows FP&A teams to focus on revenue-focused tasks like analysis and strategy development.
Automation can also speed up invoice approvals by routing reports to the right people based on predefined workflows. With controlled access, finance teams can approve invoices on their mobile devices and address any issues directly within the application, ensuring timely approvals and smooth payment cycles.
Increased accuracy and fewer errors
Automated reporting pulls information from multiple data sources, such as Excel or your ERP, saving time and reducing the need to switch between programs and compile data manually.
When finance team members spend hours on data entry, mistakes are inevitable and often difficult to detect and correct. By automating financial reporting, you ensure data accuracy by minimizing the risk of human error.
More accurate data means accurate reporting, budgeting, and forecasting.
Greater transparency and improved fraud prevention
Automated financial reporting systems can record every transaction and change made within the system, allowing you to trace all changes back to their source. FP&A teams can use this traceability to identify any unusual activity, making it easier to detect issues before they escalate.
FP&A teams can also use automated financial reporting systems to generate reports that provide a transparent and detailed overview of the company’s financial health. FP&A teams can share this report with investors, management teams, and regulatory bodies.
Since automated financial reporting systems limit human interference, bad actors will have a harder time altering the company’s financial reports, effectively reducing fraud.
How is financial reporting automated?
FP&A teams automate financial reporting using software that integrates with the company’s existing financial systems, like FP&A software, data management tools, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
These platforms can help automate:
- Data capture: Uses advanced optical character recognition (OCR) and automated workflows to capture and extract data from invoices, receipts, bank statements, and other financial documents and sources such as Gmail, Dropbox, and more
- Data integration: Connects to different data sources, such as ERP systems, databases, and spreadsheets, to gather financial data in real time without manual input
- Data validation: Checks the data for accuracy and flags any discrepancies
- Data processing: Starts automated processes involving currency conversions, calculating financial metrics, or categorizing transactions
- Report generation: Generates financial reports automatically using already predefined templates, which could include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets
- Analysis and insights: Provides valuable insights while identifying trends, anomalies, and potential areas of concern to the company
- Distribution: The system sends the report to all relevant stakeholders through available channels, such as emails or secure portals
What areas of financial reporting can be automated?
With all of those tasks automated, it’s easier for finance teams to:
- Create financial statements: Finance teams can automate the preparation of key financial statements, including cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements. Automated reporting systems pull data directly from all integrated systems to ensure the information is accurate.
- Conduct statement analysis: Automated financial reporting systems can analyze financial statements to identify trends. They can compare current and historical company data to help discover changes in revenue, cash flow, or expenses. FP&A teams can use this to discover areas that require attention and make data-backed decisions.
- Generate financial reports: Automated financial reporting software can generate different financial reports, such as management reports, budget variances, and more. FP&A teams can send these reports to key stakeholders, allowing for real-time reporting and up-to-the-minute insights into the company’s financial performance.
- Manage regulatory compliance: It can automatically generate reports that match up with the standards set by the governing bodies, such as the Government Accounting Standards Board (GASB) and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
- Input data: The software uses technology like OCR to eliminate the need for manual data entry by capturing data from various sources, including receipts, bank statements, and invoices.
Streamline reporting with Cube’s free statement of cash flow template.

Challenges to implementing automation in your financial reports
Finance teams face various challenges when implementing automation in their financial reports. Let’s take a look at some of the challenges:
System compatibility and integration
Some organizations still rely on legacy systems (an outdated computing system, either hardware or software still in use) for critical operations, despite their inefficiency and limitations. Many of these legacy systems may not be compatible with modern automated financial reporting software. Fixing this will require multiple upgrades, technical adjustments, and working with vendors who understand the specifics of the problems and how to fix them.
Technical knowledge and retraining
Implementing modern automated financial reporting software is like adopting any new technology—it requires time and effort to train your team. While the learning curve may be steep, providing your team with hands-on training, whether through third-party providers or in-house resources, helps them quickly adapt.
This investment in training boosts efficiency by reducing manual errors, speeding up report generation, and improving data accuracy, ultimately driving a strong return on investment through cost savings and better decision-making.
Data security and oversight
Like other software, automated financial reporting systems can be susceptible to cyber attacks, including data breaches, malware, and phishing attacks. Organizations can implement robust security measures, including data encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and stringent user access controls, to mitigate these risks. Look for automation tools that provide real time threat monitoring, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
Change management requirements
Resistance to change, lack of clear communication, and insufficient stakeholder engagement can hinder the adoption of new systems. Change management is necessary to solidify changes in an organization.
For this to work, provide clear communication among all the teams involved, from the management to the finance teams. You should explain the new system's benefits to the stakeholders and show how it will improve efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance. Also, offer comprehensive training programs to equip your team with the necessary skills and confidence to use the new tools effectively. Additionally, engage key stakeholders early to secure their buy-in and support, making the transition smoother for everyone.
Best practices for implementing automated financial reporting tools
Let’s take a look at some of the best practices for automated financial reporting.
1. Assess current process
Start by evaluating your current financial reporting processes. This will involve you doing the following:
- Mapping out your workflow: Start by documenting every step of your reporting process—from initial data collection to final report generation. Identify where inefficiencies occur, such as manual data entry or time-consuming reconciliations. For example, if reconciling accounts takes up too much time, this could be a key area for automation.
- Identifying pain points: Look for recurring issues that slow down your process or increase the risk of errors. Are there bottlenecks in data processing? Is report accuracy compromised due to manual interventions? Identifying these pain points can help you better understand areas where you need improvements.
- Selecting areas to improve upon: Focus on areas where automation can make a significant impact, like reducing errors or speeding up report generation
2. Identify relevant financial reporting tools
Once done, you can research and choose the best automation tool that suits your company's needs. When choosing a tool, look for:
- API integrations with your legacy systems
- Pre-built connectors and templates to popular financial software and ERPs
- A straightforward and relatively quick implementation process
- A tool with robust security measures such as end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits
- A user-friendly interface and customizable dashboards
3. Configure or customize the tech solution for your organizational needs
Start by setting up templates for reports you frequently generate. These might include income statements, cash flow summaries, or management reports. Then, define workflows for tasks like approvals and data validation to ensure your chosen tool uses clean data for effective results. Steps for proper data validation include creating clear data standards, setting review schedules, standardizing collection and storage, and adding automated checks.
Finally, make sure dashboards display metrics that matter most to your team, such as:
- Budget variances
- Cash flow trends
- Revenue growth
- Profit margins
- Operating expenses
- Accounts receivable/payable
Customizing the tool up front ensures it aligns with your processes and delivers the insights your team needs to make decisions confidently.
4. Conduct a pilot test and gather team feedback to refine processes
Before launching the tool across your entire organization, run a pilot test with a smaller group of users. Use the test to work out any issues with how the tool operates or integrates into your existing workflows.
Ask the team involved in the pilot to provide specific feedback on what works well and what doesn’t. Are the reports easy to generate? Does the tool save them time? Use their responses to identify adjustments that improve its usability and effectiveness.
5. Fine-tune tool configurations
After gathering feedback from the pilot, focus on refining the tool’s configuration. Small adjustments, like tweaking workflows or recalibrating data mappings, can significantly improve the tool's efficiency.
The goal here is to make sure the tool feels intuitive and supports your team’s day-to-day activities. By fine-tuning the setup, you can reduce frustration and set the stage for a smoother organization-wide rollout.
6. Train your team and encourage collaboration
Automated financial reporting software can take some time to learn. Provide technical training to your finance team and foster a culture of continuous learning. Motivate them to ask questions and provide feedback.
You should also encourage collaboration among finance teams. Give them a chance to learn from each other. You can even designate an automation champion in your organization so they can support and help their colleagues.
7. Ensure data quality and adhere to accounting standards
Quality data means quality reporting. Maintain the integrity of your financial reports by ensuring data accuracy and consistency. Validate data sources regularly, correct discrepancies, and ensure all reporting aligns with relevant accounting standards and regulations.
Key features of automated reporting software
There are many types of automated reporting software, each offering different functionalities, but they should all provide core capabilities that streamline financial processes and enhance decision-making. These tools are designed to save time, improve accuracy, and provide actionable insights to FP&A teams, regardless of the specific platform used.
Real-time data integration and aggregation
Automated reporting software connects directly to financial systems, pulling in data as it becomes available. There’s no need to wait for manual updates or reconcile dozens of spreadsheets. Instead, it consolidates data from multiple sources and ensures it’s always up-to-date.
This feature gives FP&A teams the confidence they need to make timely decisions because they’re working with real-time numbers. Whether it’s for forecasting, planning, or reporting, having immediate access to accurate data means fewer delays and more informed choices.
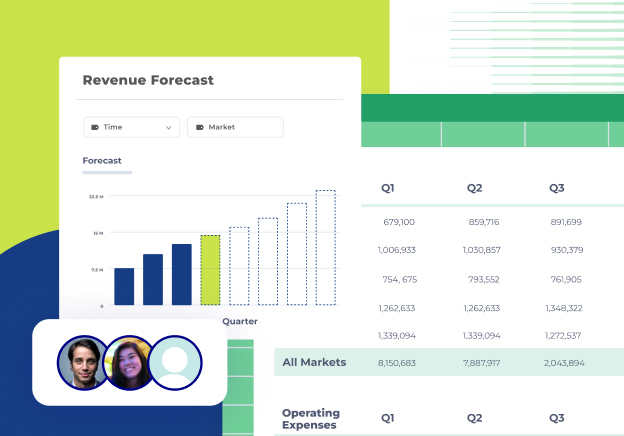
Pre-built templates and customizable dashboards
Automated financial reporting tools often include pre-built templates and customizable dashboards to streamline reporting and data visualization. Pre-built templates provide ready-to-use formats for common financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow summaries. These templates follow industry best practices, ensuring accuracy and compliance without the need for manual formatting.
Customizable dashboards offer flexibility to highlight the most relevant financial metrics and KPIs for an organization. With features like drag-and-drop functionality, interactive charts, and filter options, users can tailor dashboards to present data in a clear and actionable way. These dashboards provide a quick snapshot of financial health, making it easy to share insights with executives, track performance trends, and make informed decisions.
Regardless of the specific tool, structured templates and adaptable dashboards ensure efficiency, accuracy, and better financial visibility.
Simplify financial reporting with these free finance templates.
Scalability
A key advantage of automated reporting software is its ability to scale alongside a business’s growth. Whether a company is managing a handful of financial reports or handling complex, multi-entity consolidations, the right tool should be able to accommodate increasing data volumes and reporting needs without compromising performance.
Scalable software ensures that as transaction volumes grow, new data sources are integrated, or reporting requirements evolve, the system can adapt seamlessly. Features like cloud-based storage, automated data syncing, and customizable reporting frameworks help businesses expand their financial reporting capabilities without requiring extensive manual adjustments.
By choosing a solution that supports scalability, organizations can future-proof their reporting processes, maintain efficiency, and ensure they have the flexibility to meet both current and long-term financial analysis needs.
Easy integrations with other software and financial data sources
Automated reporting software is built to work well with the tools finance teams already rely on. Whether you’re using an enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), or spreadsheet-based system, the software integrates smoothly to bring all your data together in one place.
By connecting seamlessly to existing systems, automated reporting tools ensure FP&A teams can focus on analysis instead of wrestling with disconnected workflows.
Best automated financial reporting tools
Let’s take a look at some of the automated financial reporting tools that can streamline financial reporting and enhance decision-making.
FP&A tools
FP&A tools help FP&A teams carry out core financial processes, including data collection, consolidation and verification, planning and forecasting, budgeting, performance monitoring, and reporting and analytics.
FP&A tools help finance teams build financial models and forecasts, provide advanced financial analysis and insights to organizations, monitor the business’s general financial performance, health, and investments, and identify and measure risks or new opportunities for business growth.
Top FP&A tools for automated financial reporting:
- Cube: Cube is a cloud-based FP&A platform that helps companies hit their numbers without having to sacrifice their spreadsheets. Cube helps your finance team work anywhere by natively integrating with Excel and Google Sheets. The platform enables you to build reports and dashboards with greater flexibility, and keep everyone on the same page.
- Datarails: Datarails is an FP&A platform that enables you to automate data collection across your organization. The platform provides financial reporting and monthly close.
- Anaplan: Anaplan provides various features for finance teams, including revenue planning, OpEx planning, headcount planning, capital planning, and zero-based budgeting.
- Vena: Vena Solutions offers financial planning and analysis, integrated business planning, financial reporting, regulatory compliance reporting, and financial close management.
FP&A tools such as Cube have functionalities that go beyond this. They can also integrate with other solutions you typically use, like ERPs, CRMs, HRISs, and business intelligence software.
ERP systems
Finance teams use ERP systems to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, risk management, and compliance. An ERP system can help finance teams plan, budget, predict, and report on the financial health of a company.
Examples of ERP systems include:
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is an integrated suite of enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management applications offered by Microsoft. It combines CRM and ERP functionalities into a single platform.
- Quickbooks Enterprise: Quickbooks Enterprise is an all-in-one accounting software with accounts receivable and payable, purchasing, and order management. It provides users with real-time insights and reports into business performance.
- Sage 300: Sage 300 is an all-in-one business management software that enables you to auto-detect unrecorded transactions, errors, and differences, and reconcile your books with bank statements.
Payment platforms
Payment platforms facilitate the processing of financial transactions, allowing businesses to manage payments efficiently.
These platforms support a range of payment methods, including credit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets, and they often integrate with accounting systems to streamline financial reporting and reconciliation processes.
Examples of payment platforms include:
- Stripe: Stripe provides a fully integrated suite of financial and payments products. It enables users to set up multi-party payments and payouts, accept and optimize payments globally, and create financial reports through APIs.
- PayPal: Paypal enables users to accept payments online and in person. Users can create reports and track everything from monthly sales activity to payment and transaction types.
- Square: Square is a digital payment platform that provides businesses with tools to process transactions, manage inventory, and handle customer payments. The platform supports various payment methods, including credit cards and mobile payments, and offers additional features like point-of-sale systems and analytics.
Expense management tools
Finance teams use expense management tools for expense reimbursement and reconciliation. These tools automate the submission, approval, and reimbursement processes, ensuring that all expenses are accurately recorded and aligned with company policies.
Examples include:
- Concur Expense: Concur Expense automates your expense reporting and lets you get more visibility into your company's spending habits. Users can see all expense data in a centralized platform and automatically capture receipts and process reports.
- Expensify: Expensify is an expense management app that manages expenses, reimburses employees, creates expense reports, and sends invoices.
- Zoho Expense: Zoho Expense enables you to create comprehensive expense reports, group reports with relevant expense types, and download reports to store on your computer.

Automate your financial reporting
Automating your financial reporting processes can transform how your finance team operates, leading to greater efficiency, accuracy, and strategic insights. By reducing manual tasks, minimizing errors, and providing real-time data, automation allows your team to focus on high-impact activities like strategic financial planning, optimizing cash flow management, and driving data-driven investment decisions.
Ready to streamline your financial reporting? Learn more about how Cube can help you achieve seamless automation and elevate your financial processes.
Request a free demo today.


.png)



.png)